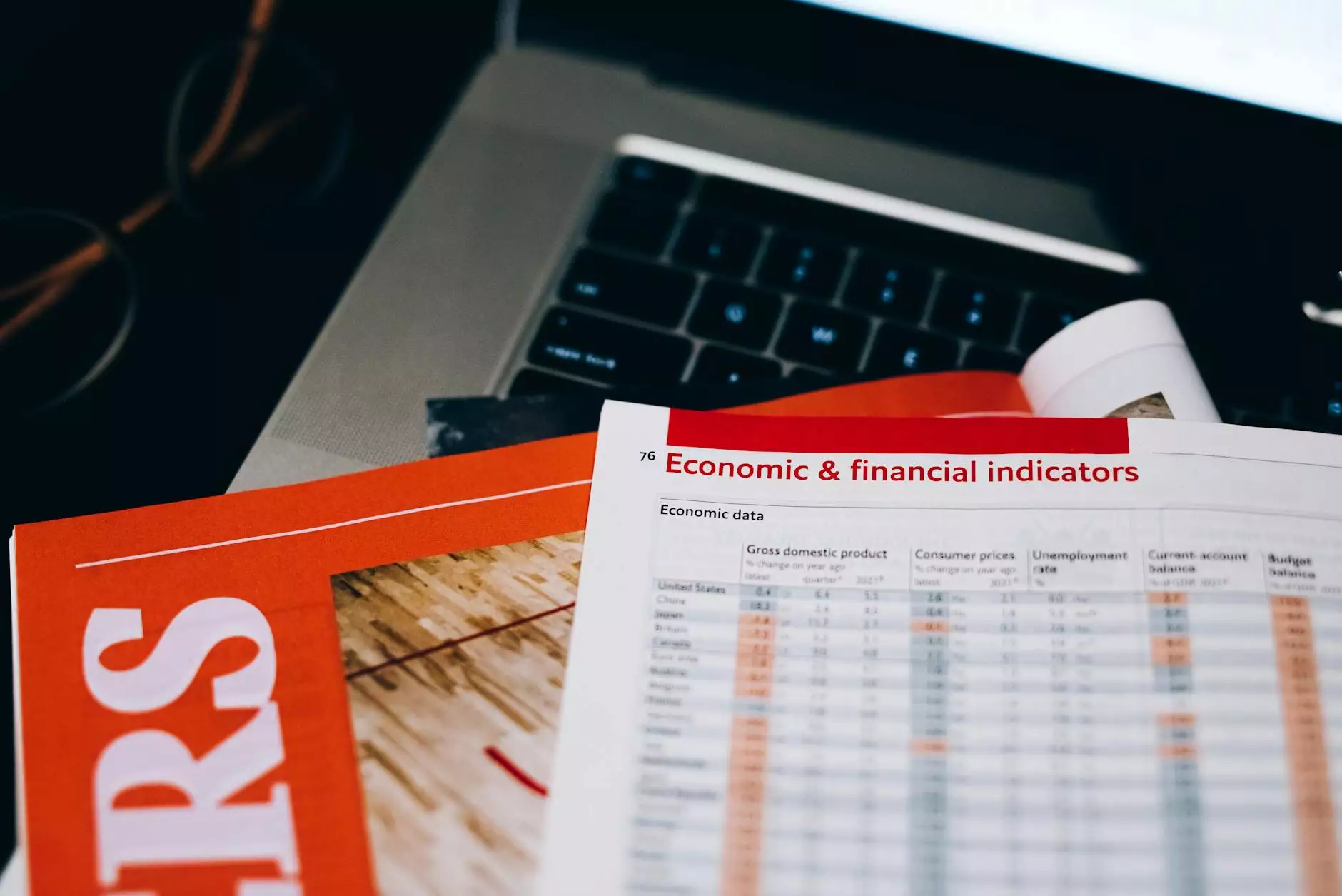
The Essential Parts of a Piston Engine

Welcome to Client-Diesel.com, your trusted destination for automotive expertise, high-end auto parts, and professional auto customization services. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate world of piston engines, exploring the various components that make them tick. Whether you're an automotive enthusiast or a professional mechanic, understanding the parts of a piston engine is key to optimizing performance and ensuring reliable operation.
1. Cylinder Block
In the heart of a piston engine lies the cylinder block, also known as the engine block or block assembly. Typically made of cast iron or aluminum alloy, the cylinder block houses the cylinders where the pistons move up and down. It serves as the foundation for numerous essential components, including the crankshaft, camshaft, and connecting rods.
2. Pistons
A piston is a cylindrical component that travels within the cylinder bore. It is connected to the crankshaft via a connecting rod and moves up and down in a reciprocating motion. Pistons are usually made from aluminum alloy, known for its lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity. They form a vital part of the combustion chamber, enabling the combustion process by compressing air and fuel, initiating power strokes.
3. Connecting Rods
Connecting rods, also referred to as con rods, play a crucial role in converting the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. These durable metal rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft, transmitting force and facilitating the transfer of energy generated from the combustion process. Made from steel or forged aluminum alloy, connecting rods need to withstand high pressures and maintain rigidity.
4. Crankshaft
The crankshaft is the backbone of the piston engine, responsible for converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. It provides the necessary power to drive the vehicle's wheels through the transmission system. Made from forged steel, the crankshaft possesses strategically placed counterweights to balance the forces generated by the pistons and connecting rods.
5. Cylinder Head
Located above the cylinder block, the cylinder head seals the top of the cylinders, forming the combustion chamber together with the piston. It contains crucial components such as intake and exhaust valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors. The cylinder head plays a crucial role in managing airflow, fuel injection, and exhaust gas removal, influencing the engine's performance, efficiency, and emissions.
6. Valves
Valves act as gatekeepers for the intake and exhaust gases in a piston engine. There are two types of valves: intake valves, which allow the air and fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber, and exhaust valves, which enable the expulsion of combustion byproducts. These valves open and close in precise synchronization with the piston's movement, guided by the camshaft.
7. Camshaft
The camshaft is a crucial component responsible for opening and closing the engine valves with precision timing. It obtains rotational power from the crankshaft through a timing belt or chain, which ensures the synchronized movement of the valves. Proper camshaft design and timing are vital to optimize engine performance and avoid interference between valves and pistons.
8. Timing Belt/Chain
The timing belt or chain, often driven by the crankshaft, plays a critical role in synchronizing the rotation of the camshaft and crankshaft. Its purpose is to ensure that the valves and pistons operate smoothly without interference. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the timing belt/chain are essential to prevent potential engine damage and maintain optimal performance.
9. Fuel Injectors
Modern piston engines employ fuel injectors to deliver precise amounts of fuel to the combustion chamber. Computer-controlled fuel injection systems ensure the efficient mixing of air and fuel for combustion. Fuel injectors operate based on signals from the engine control unit (ECU), optimizing fuel delivery and promoting better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and improved overall engine performance.
10. Spark Plugs
In gasoline engines, spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber by producing an electric spark. This controlled ignition initiates the power stroke, driving the piston down and generating rotational force on the crankshaft. Spark plugs need to withstand high temperatures and pressure while maintaining the integrity of the spark gap to ensure efficient combustion.
Conclusion
Understanding the parts of a piston engine is vital for automotive enthusiasts and professionals alike. The components mentioned above represent just a fraction of the intricate inner workings of these powerful machines. At Client Diesel, we recognize the significance of each part and its contribution to overall engine performance.
By providing high-quality auto parts for all your automotive needs, including customizations and upgrades, Client Diesel ensures that your vehicle operates at its best. Our commitment to excellence extends beyond mere product offerings, as our team of skilled technicians is ready to assist you with expert advice and professional services tailored to your specific requirements.
Visit Client-Diesel.com today to explore our wide range of auto parts and supplies, as well as our unrivaled auto customization options. Experience the difference that genuine expertise and top-notch products make in enhancing your automotive journey.
parts of the piston engine